Testosterone, often referred to as the “male hormone,” plays a crucial role in various aspects of men’s health, including muscle mass, bone density, mood regulation, and energy levels. When testosterone levels dip below the normal range, it can have significant implications for overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the effects of low testosterone in men and discuss practical strategies to increase and maintain healthy testosterone levels.
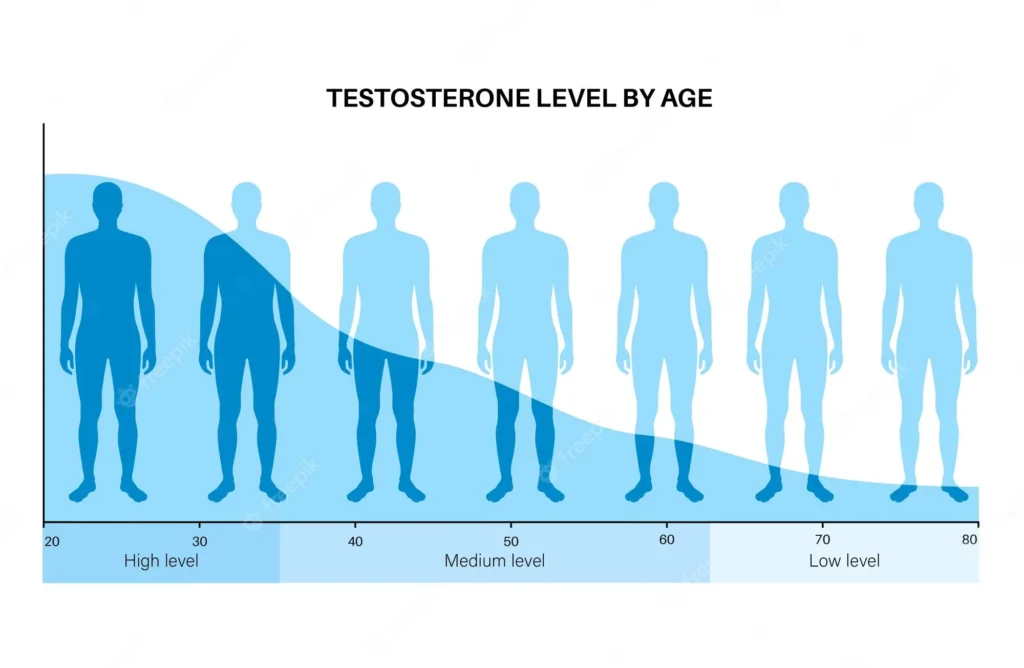
The Effects of Low Testosterone in Men:
1. Decreased Energy Levels: Testosterone is a key driver of energy and vitality. Low levels may lead to persistent fatigue, reduced stamina, and a general lack of motivation.
2. Loss of Muscle Mass: Testosterone is vital for the development and maintenance of lean muscle mass. Low levels can contribute to muscle atrophy and difficulty in building and retaining muscle.
3. Bone Density Reduction: Testosterone plays a role in maintaining bone density. Insufficient levels may result in weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
4. Mood Changes: Testosterone influences mood and emotional well-being. Low levels can contribute to irritability, mood swings, and an increased risk of developing conditions like depression.
5. Reduced Libido: Testosterone is a key player in sexual health, influencing libido and erectile function. Low levels can lead to a decline in sexual desire and performance.
Strategies to Increase Your Testosterone Levels:
1. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, especially resistance training, has been shown to boost testosterone levels. Aim for a mix of aerobic and strength-training exercises to maximize hormonal benefits.
2. Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall health, including hormone regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night to support optimal testosterone production.
3. Balanced Nutrition: Ensure your diet includes sufficient nutrients such as zinc, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are associated with healthy testosterone levels. Include a variety of whole foods, lean proteins, and vegetables in your meals.
4. Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances, including low testosterone. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to help manage stress levels.
5. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is associated with lower testosterone levels. Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to support hormonal balance.
6. Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can negatively impact testosterone levels. Moderation is key, so limit alcohol consumption to promote overall health and hormonal balance.
7. Consider Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend TRT to address clinically low testosterone levels. This involves medical supervision and should be considered after thorough consultation with a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Understanding the effects of low testosterone and adopting lifestyle strategies to support healthy levels is crucial for men’s overall well-being. By incorporating regular exercise, adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, stress management, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, men can take proactive steps to optimize their hormonal health. Remember, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach based on individual health needs and circumstances. Prioritizing hormonal health contributes not only to physical vitality but also to emotional and mental well-being, fostering a balanced and fulfilling life.